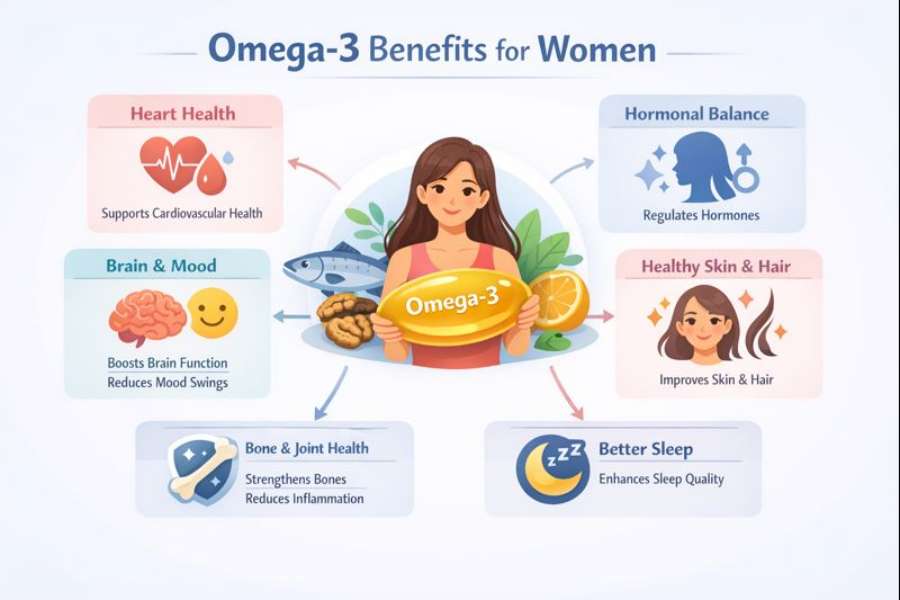
Omega-3 fatty acids play a quiet but powerful role in women’s health. From hormone balance and heart protection to brain function, pregnancy, and aging, these essential fats influence systems that women rely on daily. Because the body cannot produce omega-3s on its own, long-term intake becomes especially important across different life stages.
- What Omega-3 Fatty Acids Are and Why Women Need Them
- Omega-3 and Hormonal Balance in Women
- Menstrual Health and Omega-3 Intake
- Omega-3 Benefits for Women with PMS and PMDD
- Cardiovascular Health and Omega-3s in Women
- Cholesterol and triglyceride management
- Blood vessel and endothelial support
- Unique benefits for women’s heart health
- Omega-3 and Brain Health in Women
- Omega-3s and Mental Health in Women
- Pregnancy and Omega-3 Benefits for Women
- Fetal brain and eye development
- Reduced risk of pregnancy complications
- Maternal health during pregnancy
- Omega-3 During Breastfeeding
- Fertility and Reproductive Health
- Omega-3 and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
- Skin Health and Omega-3 Benefits for Women
- Hair and Nail Health
- Omega-3 and Bone Health in Women
- Omega-3 Benefits During Menopause
- Weight Management and Metabolic Health
- Immune Function in Women
- The Single Most Important Benefits of Omega-3 for Women
- Dietary Sources of Omega-3 for Women
- Omega-3 Supplements: Considerations for Women
- Safety and Side Effects
- Long-Term Omega-3 Intake and Consistency
- How Women Can Optimize Omega-3 Benefits
- Final Thoughts on Omega-3 Benefits for Women
This article explores the scientifically supported benefits of omega-3s for women, how they affect the female body differently from the male body, and why consistent intake matters far beyond general wellness trends.
What Omega-3 Fatty Acids Are and Why Women Need Them
Omega-3 fatty acids are a group of polyunsaturated fats essential for normal cellular function. They are considered “essential” because the body cannot synthesize them independently.
The three main types of omega-3s
ALA is found in plant sources such as flaxseed and walnuts. EPA and DHA are primarily found in fatty fish and marine oils. While the body can convert ALA into EPA and DHA, this process is inefficient, particularly in women with nutritional or hormonal imbalances.
Why omega-3 needs differ for women
Women experience unique physiological changes related to menstruation, pregnancy, breastfeeding, and menopause. Omega-3s interact with estrogen signaling, inflammatory pathways, and neural tissue in ways that directly influence female health outcomes.
Omega-3 and Hormonal Balance in Women
Hormones regulate nearly every system in the female body, and omega-3s play a supportive role in hormonal stability.
Interaction with estrogen pathways
Omega-3 fatty acids influence how estrogen is metabolized and how estrogen receptors respond in tissues. Balanced estrogen signaling is essential for menstrual regularity, mood stability, and long-term reproductive health.
Impact on inflammation and hormone-related symptoms
Many hormone-related symptoms such as cramps, breast tenderness, and cyclical discomfort are driven by inflammatory processes. Omega-3s help modulate inflammatory signaling, reducing the intensity of these symptoms over time.
Menstrual Health and Omega-3 Intake
Menstrual health is one of the most researched areas regarding omega-3 benefits for women.
Reduction in menstrual pain
Studies consistently show that omega-3 supplementation can reduce the severity of menstrual cramps. This effect is linked to reduced prostaglandin production, which plays a central role in uterine contractions and pain.
Regulation of cycle-related discomfort
Omega-3s may help stabilize mood changes, bloating, and fatigue associated with the menstrual cycle by supporting neurotransmitter balance and reducing systemic inflammation.
Omega-3 Benefits for Women with PMS and PMDD
Premenstrual symptoms vary widely in severity. Omega-3s appear particularly helpful for women with more pronounced symptoms.
Mood stabilization
Omega-3s support serotonin and dopamine signaling in the brain. This may reduce irritability, anxiety, and low mood that often appear in the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle.
Physical symptom relief
Breast tenderness, headaches, and joint discomfort may be reduced through omega-3-mediated anti-inflammatory effects.
Cardiovascular Health and Omega-3s in Women
Heart disease remains a leading cause of death among women, yet symptoms and risk patterns differ from men.
Cholesterol and triglyceride management
Omega-3s help lower triglyceride levels and improve lipid profiles. This effect is particularly important for women after menopause, when cardiovascular risk rises sharply.
Blood vessel and endothelial support
Omega-3 fatty acids improve blood vessel flexibility and reduce arterial inflammation, contributing to better circulation and lower blood pressure over time.
Unique benefits for women’s heart health
Women often develop heart disease later in life, making long-term preventive strategies critical. Omega-3 intake throughout adulthood contributes to cumulative cardiovascular protection.
Omega-3 and Brain Health in Women
The female brain shows distinct structural and chemical differences influenced by hormones. Omega-3s are deeply involved in neural health.
Cognitive function and memory
DHA is a major structural component of brain tissue. Adequate intake supports memory, focus, and cognitive resilience, particularly during periods of hormonal fluctuation.
Mental clarity across life stages
Women experience cognitive changes during pregnancy, postpartum periods, and menopause. Omega-3s support neuronal communication and may help stabilize cognitive performance.
Omega-3s and Mental Health in Women
Women are statistically more likely to experience anxiety and depression. Omega-3s have been studied extensively in this context.
Depression and mood regulation
Omega-3 fatty acids influence neurotransmitter function and neuroinflammation. Several studies suggest that women with higher omega-3 intake report fewer depressive symptoms.
Stress response and emotional resilience
Omega-3s may moderate cortisol response to stress, helping women manage emotional load more effectively over time.
Pregnancy and Omega-3 Benefits for Women
Omega-3 intake becomes especially important during pregnancy.
Fetal brain and eye development
DHA is critical for fetal neurological and visual development. Adequate maternal intake supports optimal brain structure and function in infants.
Reduced risk of pregnancy complications
Omega-3s have been associated with lower risk of preterm birth and may support healthy placental function.
Maternal health during pregnancy
Omega-3 intake may help manage inflammation, support cardiovascular health, and reduce postpartum mood disturbances.
Omega-3 During Breastfeeding
Omega-3 status during breastfeeding directly affects infant nutrition.
DHA transfer through breast milk
DHA content in breast milk depends on maternal intake. Higher omega-3 consumption supports infant cognitive and visual development.
Postpartum recovery for mothers
Omega-3s may support mood stabilization, reduce inflammation, and promote recovery after childbirth.
Fertility and Reproductive Health
Omega-3 fatty acids influence multiple aspects of reproductive health.
Egg quality and ovarian function
Healthy fats are essential for cell membrane integrity. Omega-3s improve egg quality and ovarian responsiveness.
Support for assisted reproduction
Some evidence suggests omega-3 intake may improve outcomes in fertility treatments by supporting hormonal and inflammatory balance.
Omega-3 and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS affects many women of reproductive age and involves metabolic and hormonal dysregulation.
Insulin sensitivity
Omega-3 fatty acids may improve insulin sensitivity, a key concern in PCOS.
Inflammatory modulation
Chronic inflammation is common in PCOS. Omega-3 intake can help reduce inflammatory markers associated with the condition.
Skin Health and Omega-3 Benefits for Women
Skin is highly sensitive to inflammatory and hormonal changes.
Skin barrier and hydration
Omega-3s support cell membrane integrity, helping skin retain moisture and resist irritation.
Acne and inflammatory skin conditions
By reducing inflammation, omega-3s may help manage acne severity and conditions such as eczema.
Aging and wrinkle formation
Long-term omega-3 intake supports skin elasticity and may slow visible signs of aging by protecting collagen structure.
Hair and Nail Health
Omega-3s support keratin production and circulation.
Hair strength and shine
Adequate omega-3 intake contributes to scalp health and hair shaft integrity, reducing dryness and breakage.
Nail resilience
Brittle nails may benefit from improved fatty acid balance, supporting stronger nail growth.
Omega-3 and Bone Health in Women
Bone health becomes a major concern after menopause.
Calcium metabolism and inflammation
Omega-3s may improve calcium utilization and reduce bone-resorbing inflammation.
Osteoporosis risk reduction
Long-term omega-3 intake may help preserve bone density, particularly when combined with adequate vitamin D and weight-bearing exercise.
Omega-3 Benefits During Menopause
Menopause brings hormonal changes that affect nearly every system.
Joint pain and stiffness
Inflammation often increases during menopause. Omega-3s can help reduce joint discomfort and improve mobility.
Mood and sleep support
Omega-3 intake may ease mood fluctuations and support sleep quality during hormonal transitions.
Cardiometabolic protection
Postmenopausal women face higher cardiovascular risk. Omega-3s offer protective support during this stage.
Weight Management and Metabolic Health
Omega-3s are not weight-loss drugs, but they influence metabolism.
Fat metabolism and insulin signaling
Omega-3s help improve metabolic flexibility and may support healthier body composition.
Appetite regulation
By influencing satiety hormones, omega-3s may help regulate appetite indirectly.
Immune Function in Women
Women often experience stronger immune responses, which can increase autoimmune risk.
Immune balance
Omega-3s help regulate immune activity, reducing excessive inflammatory responses without suppressing immunity.
Autoimmune considerations
Women with autoimmune tendencies may benefit from the immunomodulatory effects of omega-3s.
The Single Most Important Benefits of Omega-3 for Women
This is the only section where bullet points are used.
-
Hormonal balance and menstrual comfort
-
Cardiovascular protection across life stages
-
Brain health and mood stability
-
Pregnancy and fetal development support
-
Skin, hair, and nail health
-
Bone strength and aging support
-
Reduced inflammation and immune balance
These benefits reflect the broad systemic role omega-3s play in women’s health.
Dietary Sources of Omega-3 for Women
Whole-food sources provide additional nutrients alongside omega-3s.
Marine sources
Fatty fish such as salmon, sardines, and mackerel provide EPA and DHA in highly bioavailable forms.
Plant sources
Flaxseed, chia seeds, walnuts, and hemp seeds provide ALA, though conversion efficiency is limited.
Omega-3 Supplements: Considerations for Women
Supplements may be useful when dietary intake is insufficient.
Fish oil vs algae oil
Algae-based omega-3 supplements provide DHA and EPA without animal sources, making them suitable for vegetarians.
Dosage considerations
Needs vary by age, pregnancy status, and health conditions. Medical guidance is recommended for higher doses.
Safety and Side Effects
Omega-3s are generally safe but should be used thoughtfully.
Gastrointestinal tolerance
Some individuals experience mild digestive discomfort, especially at higher doses.
Medication interactions
Omega-3s may interact with blood-thinning medications. Medical supervision is advised when combining therapies.
Long-Term Omega-3 Intake and Consistency
Benefits of omega-3s accumulate over time.
Short-term vs long-term intake
Occasional intake offers limited benefit. Consistent consumption supports structural and functional health across systems.
Life-stage adaptation
Omega-3 needs evolve from adolescence through menopause and beyond.
How Women Can Optimize Omega-3 Benefits
Lifestyle context matters.
Balanced nutrition
Omega-3s work best within a nutrient-dense diet.
Physical activity
Exercise enhances many omega-3 benefits, particularly for cardiovascular and mental health.
Medical guidance
Individual needs vary. Personalized advice improves outcomes.
Final Thoughts on Omega-3 Benefits for Women
Omega-3 fatty acids support women’s health in ways that extend far beyond basic nutrition. From hormonal balance and heart protection to brain function, skin health, and aging, their influence is broad and deeply integrated into female physiology.
Consistent, adequate omega-3 intake represents a long-term investment in health at every stage of life. When combined with balanced nutrition, physical activity, and medical guidance, omega-3s offer meaningful support for women seeking resilience, vitality, and well-being over time.